Step-by-step explanation:
The equation for osmotic pressure, which is:
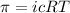
where,
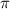 = osmotic pressure of the solution
= osmotic pressure of the solution
i = Van't hoff factor
c = concentration of solute
R = Gas constant =
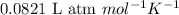
T = temperature of the solution
a). Solution A: 0.10M NaCl(aq) , Solution B: 0.10M KBr (aq)
Solution A: 0.10M NaCl(aq)
i = 2, (100% dissociation for electrolytes)
T = 20°C= 20 + 273 K = 293 K
c = 0.10 M
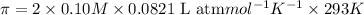
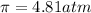
Solution B: 0.10M KBr(aq)
i = 2, (100% dissociation for electrolytes)
T = 20°C= 20 + 273 K = 293 K
c = 0.10 M
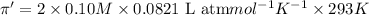
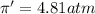
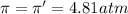 (no flow of water will occur)
(no flow of water will occur)
b). Solution A: 0.10M
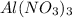 , Solution B: 0.20M
, Solution B: 0.20M
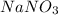
Solution A: 0.10M
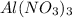
i = 4, (100% dissociation for electrolytes)
T = 20°C= 20 + 273 K = 293 K
c = 0.10 M
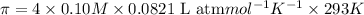
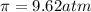
Solution B: 0.10M
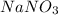
i = 2, (100% dissociation for electrolytes)
T = 20°C= 20 + 273 K = 293 K
c = 0.10 M
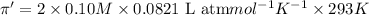
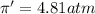
Flow of water will occur from solution B to solution A.
c). Solution A: 0.10M
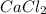 , Solution B: 0.50M
, Solution B: 0.50M
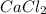
Solution A: 0.10M
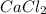
i = 3, (100% dissociation for electrolytes)
T = 20°C= 20 + 273 K = 293 K
c = 0.10 M
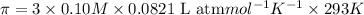
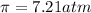
Solution B: 0.50M
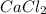
i = 3, (100% dissociation for electrolytes)
T = 20°C= 20 + 273 K = 293 K
c = 0.50 M
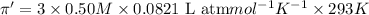
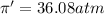
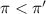
Flow of water will occur from solution A to solution B.