Step-by-step explanation:
According to Bronsted-Lowry an acid is defined as the specie which is able to donate hydrogen ions when dissolved in water.
For example,
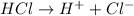
On the other hand, bases are the species which are able to donate hydroxide ions when dissolved in water.
For example,
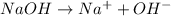
A specie which is able to accept a hydrogen atom and also able to donate a hydroxide ion will act as both acid and a base.
For example,
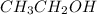 is able to donate a hydroxide ion and simultaneously can accept a hydrogen ion.
is able to donate a hydroxide ion and simultaneously can accept a hydrogen ion.
In
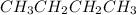 , the hydrogen atoms are strongly held together by the carbon atoms due to the small electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen atom. Hence, it will be a weak acid.
, the hydrogen atoms are strongly held together by the carbon atoms due to the small electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen atom. Hence, it will be a weak acid.
On the other hand,
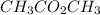 can loose a hydrogen atom or it can also gain a hydroxyl group. This is due to the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen atom.
can loose a hydrogen atom or it can also gain a hydroxyl group. This is due to the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen atom.
Thus, we can conclude that following compounds are classified as follows.
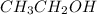 - can be both acid and base
- can be both acid and base
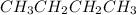 - very weak acid
- very weak acid
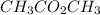 - can be both acid and base
- can be both acid and base