Answer:
A) 2 x + 10 x = 2x ( 1 + 5)
B) -4(3 x - 10)+5 (2 - 6 x) =2 ( -21 x + 25)
C) 2(x-4)+x = 3 x - 8
D) -3 -7(3 -4 x) + 8 x = 12 (3 x - 2)
Explanation:
DISTRIBUTIVE PROPERTY:
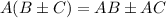
Now, here the given expressions are:
A. 2 x+ 10 x
Here, in 2 x + 10 x tale (2 x) as a common factor.
⇒2 x + 10 x = 2 x ( 1 + 5)
So, by distributive property: 2 x + 10 x = 2x ( 1 + 5)
B. -4(3 x - 10)+5 (2 - 6 x)
Here, solving the given expression, we get:
-4(3 x - 10)+5 (2 - 6 x) = -4(3 x) -4(-10) + 5(2) +5 (-6x)
= - 12 x + 40 + 10 - 30 x = -42 x + 50
Now, take (2) as common factor, we get: -42 x + 50 =2 ( -21 x + 25)
So, by distributive property: -4(3 x - 10)+5 (2 - 6 x) =2 ( -21 x + 25)
C. 2(x-4)+x
Here, solving the given expression, we get:
2(x-4)+x = 2(x) - 2(4) + x = 2 x - 8 + x = 3 x - 8
Hence, 2(x-4)+x = 3 x - 8
D. -3-7(3-4x)+8x
Here, solving the given expression, we get:
-3-7(3-4x)+8x = -3 -(7(3) + 7(-4)) + 8 x = -3 - 21 + 28 x + 8 x = 36 x - 24
Now, take (12) as common factor, we get : 36 x - 24 = 12 (3 x - 2)
Hence -3 -7(3 -4 x) + 8 x = 12 (3 x - 2)