Answer:
All the calculations are shown in the explanation
Step-by-step explanation:
RLC Circuit
The circuit proposed in the problem consists in one resistor R in series with the parallel of a capacitor C and an inductor L. All the impedances, voltages, currents and powers must be expressed as complex numbers since they all have an active and a reactive component. The formulas are very similar to those of the Ohm's law, as will be shown below.
The source has a time function expressed as
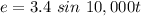
We must find the RMS voltage as
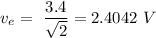
The given parameters of the circuit are
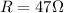
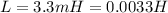
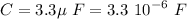
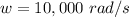
(a)
Let's find the reactances
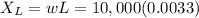

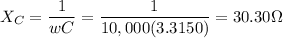
Now the impedances are
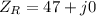
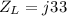
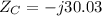
The equivalent impedance of the parallel of the capacitor and the inductor is
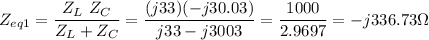
Computing the total impedance of the circuit
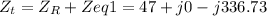

Converting to phasor form
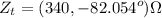
The given voltage of the source is
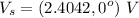
It has an angle of 0 degrees since it's the reference. Let's compute the total current of the circuit
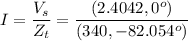
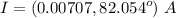
We can see the current leads the voltage, so our circuit has a capacitive power factor, as shown ahead .
The voltage acrosss the resistor is
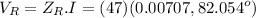
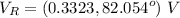
The currents through the capacitor and inductor will be computed with the formula of the current divider .
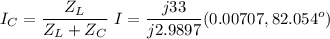
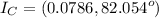
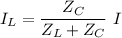
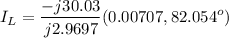
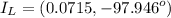
(b) The aparent power from the source is the product of the voltage by the total current
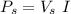
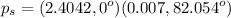
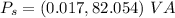
Finally, the power factor is
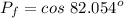
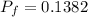
As mentioned before, since the current leads the voltage, the circuit is primarily capacitive