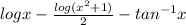Answer:
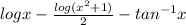
Explanation:
step 1:- by using partial fractions
/(x(x^(2)+1) ) =(A(x^(2)+1)+(Bx+C)(x )/(x(x^(2)+1) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/67jvn5wv6x1f7ltxikaqrqs8pvc3mfj7mo.png) ......(1)
......(1)
step 2:-
solving on both sides
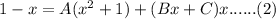
substitute x =0 value in equation (2)
1=A(1)+0
A=1
comparing x^2 co-efficient on both sides (in equation 2)
0 = A+B
0 = 1+B
B=-1
comparing x co-efficient on both sides (in equation 2)
-1 = C
step 3:-
substitute A,B,C values in equation (1)
now
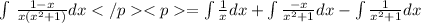
by using integration formulas
i) by using
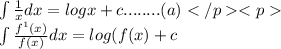 .....(b)
.....(b)
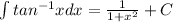 .....(c)
.....(c)
step 4:-
by using above integration formulas (a,b,and c)
we get answer is