Answer:
The correct answer is option B.
Step-by-step explanation:
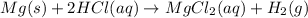
Temperature of the hydrogen gas = T = 25°C=25+273 K= 298 K
Pressure of hydrogen gas ,P = gauge pressure - vapor pressure of water
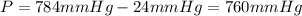
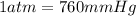
Volume of the hydrogen gas = V =100 mL =100 × 0.001 L= 0.1 L
(1 mL = 0.001 L)
Moles of hydrogen gas = n
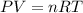 (ideal gas equation )
(ideal gas equation )
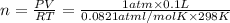
n =
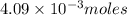
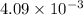 moles of hydrogen are produced in this reaction.
moles of hydrogen are produced in this reaction.