Answer:
9. x = 31°
10. m∠ABC = 62°
11. m∠BCA = 60°
Explanation:
We are given the following values for ΔABC, and its exterior angle, ∠ACD:
In ΔABC, the two nonadjacent interior angles are:
While the exterior angle, m∠ACD = (5x - 35)°.
In order to solve for questions 9 through 11, we must apply the Exterior Angle Theorem which states that the measure of the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent or remote interior angles.
Question 9:
In order to find the value of x, we can use the Exterior Angle Theorem:
m∠ACD = m∠A + m∠B
(5x - 35)° = 58° + 2x°
5x° - 35° = 58° + 2x°
Subtract 2x from both sides:
5x° - 2x - 35° = 58° + 2x° - 2x
3x - 35° = 58°
Next, add 35° to both sides:
3x° - 35° + 35° = 58° + 35°
3x° = 93°
Divide both sides by 3 to isolate x:
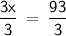
x = 31°
Therefore, the value of x = 31°.
Question 10:
In order to find m∠ABC, we must first substitute the value of x into m∠B:
m∠B = 2x° = 2(31)° = 62°
Therefore, m∠ABC = 62°.
Question 11:
In order to find m∠BCA, we must first find the value of its supplement, m∠ACD, by substituting the value of x derived from question 9.
m∠ACD = 5x° - 35° = 5(31)° - 35° = 120°
Next, substitute the value of m∠ACD into the following equation:
m∠BCA + m∠ACD = 180°
m∠BCA + 120° = 180°
Subtract 120° from both sides:
m∠BCA + 120° - 120° = 180° - 120°
m∠BCA = 60°
Therefore, m∠BCA = 60°.
Verify:
In order to verify whether we have the correct values for each interior angles, we can apply the Triangle Sum Theorem which states that the sum of all interior angles of a triangle is equal to 180°. In other words:
m∠A + m∠B + m∠C = 180°.
58° + 62° + 60° = 180°
180° = 180° (True statement).