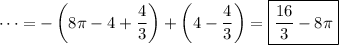By Green's theorem, the line integral of F along C is equal to the integral of the curl of F (two-dimensional curl, that is) over the region bounded by C, where C is a generic path that is oriented counterclockwise. However, our C run clockwise, so we multiply the following by -1.
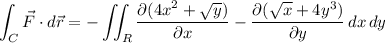
where R is the set
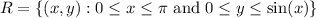
Compute the double integral:
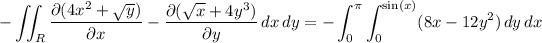
Integrating with respect to y is trivial:
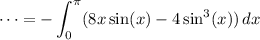
Integrating by parts with
u = x ⇒ du = dx
dv = sin(x) dx ⇒ v = -cos(x)
gives
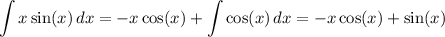
while in the other integral, we have by substitution
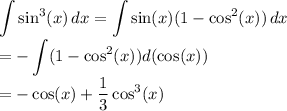
Then our last integral evaluates to