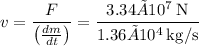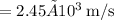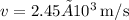
Step-by-step explanation:
Newton's 2nd Law can be expressed in terms of the object's momentum, in this case the expelled exhaust gases, as
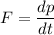 (1)
(1)
Assuming that the velocity remains constant then
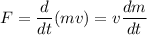
Solving for
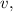 we get
we get
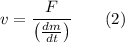
Before we plug in the given values, we need to convert them first to their appropriate units:
The thrust F is
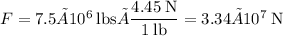
The exhaust rate dm/dt is
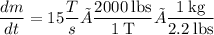
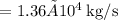
Therefore, the velocity at which the exhaust gases exit the engines is