With a $4,500 investment at 5.75% interest compounded semi-annually, it takes approximately 7.9 years for the money to grow to $10,000.
To determine how long it takes for the investment to reach $10,000 with a 5.75% interest rate compounded semi-annually, we can use the compound interest formula:
![\[A = P \left(1 + (r)/(n)\right)^(nt)\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/b8ruh2jvdg2xg92qmgf5d8bf1j3cycbva2.png)
Where:
-
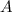 is the future value of the investment
is the future value of the investment
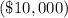 ,
,
-
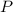 is the principal amount
is the principal amount
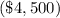 ,
,
-
 is the annual interest rate (5.75% or 0.0575 as a decimal),
is the annual interest rate (5.75% or 0.0575 as a decimal),
-
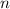 is the number of times interest is compounded per year (2 for semi-annual),
is the number of times interest is compounded per year (2 for semi-annual),
-
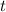 is the time the money is invested for in years.
is the time the money is invested for in years.
Rearranging the formula to solve for
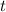 :
:
![\[t = (\log(A/P))/(n \cdot \log(1 + (r)/(n)))\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/wa7eq8pa4ci0gujh21qhm3eoy2kg8c4mfj.png)
Now, we can substitute the given values:
![\[t = (\log(10,000/4,500))/(2 \cdot \log(1 + (0.0575)/(2)))\]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/eoo7tnbawstdlq1wi4aedznovhjfi7h0lf.png)
Calculating this expression gives approximately
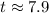 years.
years.
Therefore, to the nearest tenth of a year, the person must leave the money in the bank for approximately 7.9 years for it to reach $10,000.