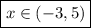1)
We note that the quadratic can be factored into
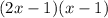 .
.
The quadratic is greater than
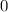 if both of its factors are positive, or they are both negative.
if both of its factors are positive, or they are both negative.
Case: both positive
We need to solve the system of inequalities:
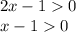 .
.
The first inequality gives
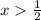 .
.
The second inequality gives
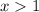 .
.
Taking the points where the inequalities coincide gives
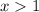 .
.
(Note: 1 is a root of the quadratic. Coincidence? If not, try and prove it!)
Case: both negative
We need to solve the system of inequalities:
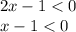 .
.
The first inequality gives
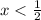 .
.
The second inequality gives
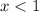 .
.
Taking the points where the inequalities coincide gives
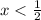 .
.
(Note:
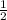 is the other root of the quadratic. Coincidence? If not, try and prove it!)
is the other root of the quadratic. Coincidence? If not, try and prove it!)
Taking the union of both cases gives the solution set:
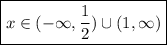
2)
We bring over the
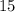 to get
to get
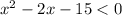 .
.
Note that the quadratic factors into
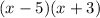 .
.
The quadratic is less than
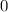 if 1 of its factors is negative, but not both.
if 1 of its factors is negative, but not both.
Case: first factor is negative, second positive
We have that
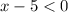 and
and
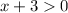 .
.
We get that
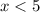 and
and
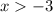 , which has the solution set
, which has the solution set
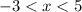 .
.
Case: second factor is negative, first positive
We have that
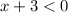 and
and
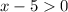 .
.
We get that
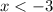 and
and
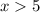 , which has no solutions.
, which has no solutions.
So, the solution set is