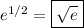You can check that both series converge for all real x (say, using the ratio test).
Now,
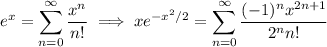
and if you have some familiarity with differential equations, you might recognize that the second series represents a Bessel function, namely
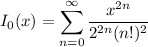
but we won't bother making use of this.
In the integral, we interchange the integral with the sum
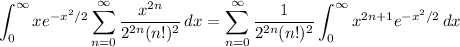
and consider the sequence of integrals,
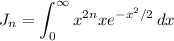
Integrating by parts with
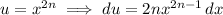
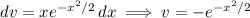
Then the contribution of uv is 0, so
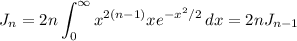
We have
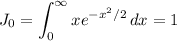
so that
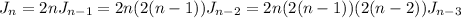
and so on; after k steps,
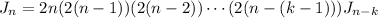
so that when n = k,
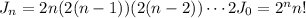
Then the integral we want is
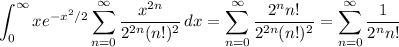
and knowing the series expansion for
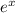 , it follows that the integral has a value of
, it follows that the integral has a value of