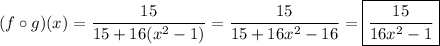First note the domains of f and g :
domain f(x) : x ≠ -16
domain g(x) : x ≠ 1, x ≠ -1
Then the domain of f ○ g is
15/(x ² - 1) ≠ -16
which can be "solved" for x :
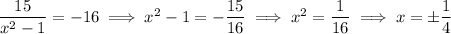
so that, in addition to domain of g, the domain of the composite function is
domain (f ○ g)(x) : x ≠ 1/4, x ≠ -1/4, x ≠ 1, x ≠ -1
The function itself can be evaluated as
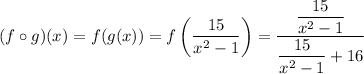
Simplifying a bit, we end up with