From the analysis of the discriminant, you obtain that the quadratic function has no real solutions.
In first place, you must know that the roots or solutions of a quadratic function are those values of x for which the expression is 0. This is the values of x such that y = 0. That is, f (x) = 0.
Being the quadratic function f (x)=a*x² + b*x + c, then the solution must be when: 0 =a*x² + b*x + c
The solutions of a quadratic equation can be calculated with the quadratic formula:
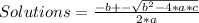
The discriminant is the part of the quadratic formula under the square root, that is, b² - 4*a*c
The discriminant can be positive, zero or negative and this determines how many solutions (or roots) there are for the given quadratic equation.
If the discriminant:
- is positive: the quadratic function has two different real solutions.
- equal to zero: the quadratic function has a real solution.
- is negative: none of the solutions are real numbers. That is, it has no real solutions.
In this case, a= -40, b=10 and c= -1. Then, replacing in the discriminant expression:
discriminant= 10² -4*(-40)*(-1)
Solving:
discriminant= 100 - 160
discriminant= -60
The discriminant is negative, so the quadratic function has no real solutions.