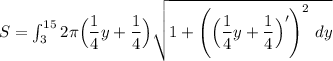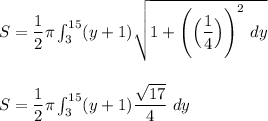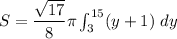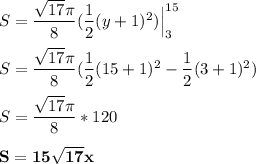Answer:
Explanation:
Let take a look at the given function y = 4x - 1 whose point is located between (1,3) and (4,15) on the graph.
Here, the function of y is non-negative. Now, expressing y in terms of x in y = 4x- 1
4x = y + 1
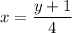
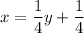
By integration, the required surface area in the revolve is:
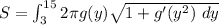
where;
g(y) =
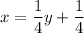
∴