Answer: The moles of gas present in the cylinder is 0.34 moles.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
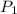 = 2.7 atm,
= 2.7 atm,
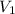 = 3.1 L,
= 3.1 L,
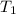 = 300 K
= 300 K
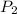 = ?,
= ?,
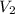 = 9.4 L,
= 9.4 L,
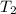 = 610 K
= 610 K
Formula used to calculate the final temperature is as follows.
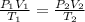
Substitute the values into above formula as follows.
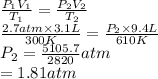
Now, moles present upon heating the cylinder are as follows.
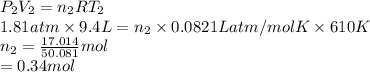
Thus, we can conclude that moles of gas present in the cylinder is 0.34 moles.