Answer:
r = 41.1 10⁹ m
Step-by-step explanation:
For this exercise we use the equilibrium condition, that is, we look for the point where the forces are equal
∑ F = 0
F (Earth- probe) - F (Mars- probe) = 0
F (Earth- probe) = F (Mars- probe)
Let's use the equation of universal grace, let's measure the distance from the earth, to have a reference system
the distance from Earth to the probe is R (Earth-probe) = r
the distance from Mars to the probe is R (Mars -probe) = D - r
where D is the distance between Earth and Mars
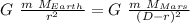
M_earth (D-r)² = M_Mars r²
(D-r) =
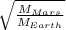 r
r
r (
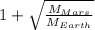 ) = D
) = D
r =
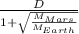
We look for the values in tables
D = 54.6 10⁹ m (minimum)
M_earth = 5.98 10²⁴ kg
M_Marte = 6.42 10²³ kg = 0.642 10²⁴ kg
let's calculate
r = 54.6 10⁹ / (1 + √(0.642/5.98) )
r = 41.1 10⁹ m