Answer: The total partial pressure of the solution is 131.37 torr.
Step-by-step explanation:
The number of moles is defined as the ratio of the mass of a substance to its molar mass. The equation used is:
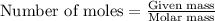 ......(1)
......(1)
Given mass of glucose = 46.8 g
Molar mass of glucose = 180 g/mol
Plugging values in equation 1:
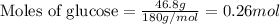
Given mass of methanol = 117 g
Molar mass of methanol = 32 g/mol
Plugging values in equation 1:
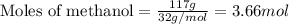
Mole fraction is defined as the moles of a component present in the total moles of a solution. It is given by the equation:
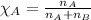 .....(2)
.....(2)
where n is the number of moles
Putting values in equation 2:
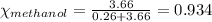
Raoult's law is the law used to calculate the partial pressure of the individual gases present in the mixture. The equation for Raoult's law follows:
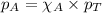 .....(3)
.....(3)
where
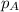 is the partial pressure of component A in the mixture and
is the partial pressure of component A in the mixture and
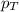 is the total partial pressure of the mixture
is the total partial pressure of the mixture
We are given:
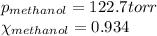
Putting values in equation 3, we get:
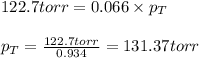
Hence, the total partial pressure of the solution is 131.37 torr.