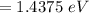Answer:
The right solution is:
(a) 2.87 eV
(b) 1.4375 eV
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Wavelength,
= 433 nm
Potential difference,
= 1.43 V
Now,
(a)
The energy of photon will be:
E =
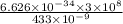
=
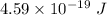
or,
=
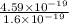
=
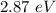
(b)
As we know,
⇒
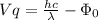
By substituting the values, we get
⇒
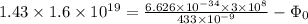
⇒
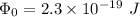
or,
⇒
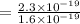
⇒