Answer:
The coordinates of E are
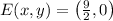 .
.
Explanation:
The triangle ABC represents a right triangle as both sides AB and AC are orthogonal to each other. The side AB is in the y axis, whereas the side AC is in the x axis. The triangle is dilated with respect to the origin, in which point A is set.
Vectorially speaking, dilation is defined by the following operation:
![P'(x,y) = O(x,y) + k\cdot [P(x,y) - O(x,y)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/kjlj0rdylbjwm7yi17nwqtahjrsn9zym95.png) (1)
(1)
Where:
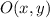 - Point of reference.
- Point of reference.
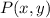 - Original point.
- Original point.
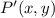 - Dilated point.
- Dilated point.
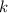 - Dilation factor.
- Dilation factor.
By applying this operation, point B becomes point D:
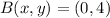 ,
,
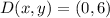
![D(x,y) = (0,0) + k\cdot [(0,4)- (0,0)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/6iqnor77f37qi7ek0lico8f5w6ztdsqj4f.png)
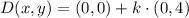
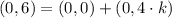
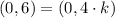
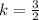
Lastly, we transform point C into point E by applying the same operation:
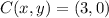 ,
,
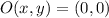 and
and
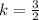
![E(x,y) = (0,0) + (3)/(2)\cdot [(3,0)-(0,0)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/1b05nkjyx3lbdvc0x58l5p0vzibrge1mj4.png)
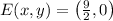
The coordinates of E are
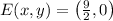 .
.