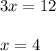Answer:
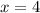
Explanation:
To solve this problem, one must use the angle bisector theorem. This theorem provides a proportion between the sides formed by an angle bisector. One can apply this theorem here by forming the following proportion,
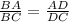
Substitute,
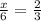
Cross products,
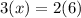
Simplify,
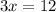
Inverse operations,