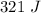Answer: 321 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
Mass of the box
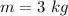
Force applied is
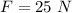
Displacement of the box is
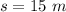
Velocity acquired by the box is
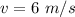
acceleration associated with it is
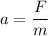
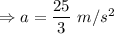
Work done by force is
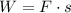
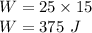
change in kinetic energy is
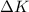
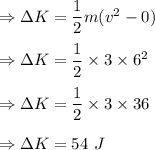
According to work-energy theorem, work done by all the forces is equal to the change in the kinetic energy
![\Rightarrow W+W_f=\Delta K\quad [W_f=\text{Work done by friction}]\\\\\Rightarrow 375+W_f=54\\\Rightarrow W_f=-321\ J](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/physics/college/36hgrsb3vb01lvvtpspjv0lzytzw2brdx7.png)
Therefore, the magnitude of work done by friction is