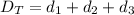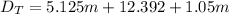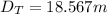Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that:
Acceleration
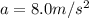
Displacement
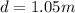
Initial time
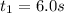
Final Time
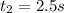
Generally the equation for Velocity of 1.05 travel is mathematically given by
Using Newton's Law of Motion
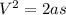

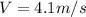
Generally the equation for Distance traveled before stop is mathematically given by
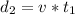
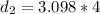
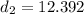
Generally the equation for Distance to stop is mathematically given by
Since For this Final section
Final velocity
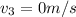
Initial velocity
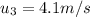
Therefore
Using Newton's Law of Motion
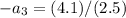
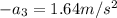
Giving
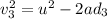
Therefore
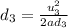
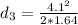
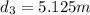
Generally the Total Distance Traveled is mathematically given by