Answer:
a. We have no information about the underlying distribution, and thus, by the Central Limit Theorem, we cannot determine probabilities for a number of beds less than 30.
b. 0.4364 = 43.64% probability that Bill finishes all 64 beds in 5 hours.
Explanation:
Normal Probability Distribution:
Problems of normal distributions can be solved using the z-score formula.
In a set with mean
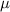 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
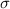 , the z-score of a measure X is given by:
, the z-score of a measure X is given by:
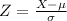
The Z-score measures how many standard deviations the measure is from the mean. After finding the Z-score, we look at the z-score table and find the p-value associated with this z-score. This p-value is the probability that the value of the measure is smaller than X, that is, the percentile of X. Subtracting 1 by the p-value, we get the probability that the value of the measure is greater than X.
Central Limit Theorem
The Central Limit Theorem establishes that, for a normally distributed random variable X, with mean
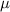 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
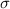 , the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
, the sampling distribution of the sample means with size n can be approximated to a normal distribution with mean
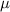 and standard deviation
and standard deviation
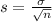 .
.
For a skewed variable, the Central Limit Theorem can also be applied, as long as n is at least 30.
Mean of 5 minutes and variance of 4 minutes (distribution not given).
This means that
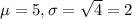
Sample of 64:
This means that
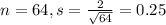
a. What is the probability that the average time it takes to prepare a bed is more than 4.5 minutes?
We have no information about the underlying distribution, and thus, by the Central Limit Theorem, we cannot determine probabilities for a number of beds less than 30.
b. One day, Bill was the only one of the morning shift who was able to get to work, due to hazardous weather conditions and illnesses. Assuming that Bill takes no breaks, what is the probability that Bill finishes all 64 beds in 5 hours?
5 hours = 300 minutes.
300/64 = 4.6875.
This is the probability of a sample mean below 4.6875, which is the p-value of Z when X = 4.6875. So
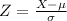
By the Central Limit Theorem
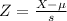
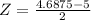

 has a p-value of 0.4364.
has a p-value of 0.4364.
0.4364 = 43.64% probability that Bill finishes all 64 beds in 5 hours.