Answer: The enthalpy change during this reaction is 77505.56 J.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
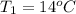 ,
,
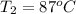
Mass = 254 g, Specific heat =
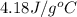
Formula used to calculate the enthalpy change is as follows.
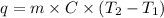
where,
q = enthalpy change
m = mass of substance
C = specific heat capacity
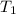 = initial temperature
= initial temperature
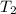 = final temperature
= final temperature
Substitute the values into above formula as follows.
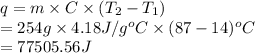
Thus, we can conclude that the enthalpy change during this reaction is 77505.56 J.