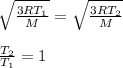Answer:
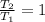
Step-by-step explanation:
The root mean square velocity of the gas at an equilibrium temperature is given by the following formula:
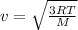
where,
v = root mean square velocity of molecules:
R = Universal Gas Constant
T = Equilibrium Temperature
M = Molecular Mass of the Gas
Therefore,
For T = T₁ :
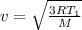
For T = T₂ :
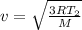
Since both speeds are given to be equal. Therefore, comparing both equations, we get: