Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
We have the three equations:
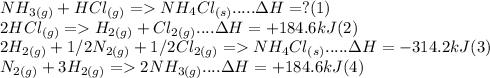
(can you double check that it is 184.6kJ for both equations 2 and 4 because it seems unlikely). We need to solve for equation 1 by addition and changing equations 2, 3 and 4. After possibly some trial and error, we can find that if we flip equations 4, multiply equation 3 by 2, add the equations together, and then finally divide by 2, we can get equation 1. We will get the answer of -314.2 kJ. However, I am again skeptical about the delta H values for equation 2 and 4 so double check that. This method might be super confusing and it is really hard to explain. So what I would suggest you to watch videos on Hess' law.