Answer:
Kp = 0.949
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the given chemical reaction:
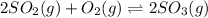
It is possible to set up the equilibrium expression as shown below:
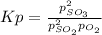
Whereas the initial pressure of SO2 was 3.43 atm and that of O2 was 1.61 atm. Now, since the partial pressure of O2 decreased to the 0.809 atm, it is possible to calculate the change in the pressure of O2 via:
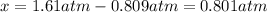
Which is actually applied to SO3 and SO2 according to the stoichiometry in the equilibrium expression to calculate Kp:
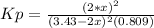
Thus, by plugging in x, we obtain:
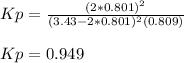
Best regards!