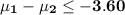Answer:
Explanation:
From the given information:
Let assume:
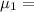 population mean for catalyst 1
population mean for catalyst 1
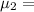 population mean for catalyst 2
population mean for catalyst 2
Then:
Null hypothesis:
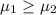
Alternative hypothesis:
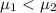
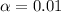
By using MINITAB software to compute the 2 sample t-test, we have:
Two-Sample T_Test and CI
Sample N Mean StDev SE Mean
1 12 94.00 3.00 0.87
2 15 90.00 2.00 0.52
Difference =

Estimate of difference: -6.00
99% upper bound for difference: -3.603
T-test of difference: 0 (vs <): T-value = -6.22
P.value = 0.000
DF = 25
Both use Pooled StDev = 2.4900
From above result
the test statistics = -6.00
p-value = 0.00
Decision Rule: To reject
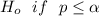
Conclusion: Provided that p-value is < ∝, we reject
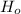 . Hence, there is sufficient evidence to support the given claim.
. Hence, there is sufficient evidence to support the given claim.
b) From the MINITAB;
The 99% C.I on the difference in the mean yields that can be applied to test the claim in part (a) is: