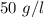Answer:
The right approach is "50 g/l".
Step-by-step explanation:
The given values are:
Mass or solute or precipitation,
= 0.15 kg
on converting it into "g", we get
=
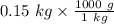
=
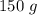
Volume of solution,
= 3.00 L
Now,
The solubility of X will be:
=
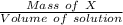
On substituting the values, we get
=
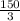
=