Answer:
There is no sufficient evidence to support the claim that men and women differ in repeatability for this assembly task
Step-by-step explanation:
Given
Let subscript 1 represent men and 2 represent women, respectively.
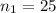
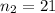
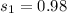
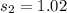
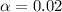
Required
Determine if here is enough evidence
First, we need to state the hypotheses
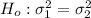
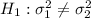
Next, calculate the test statistic using:
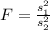
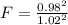
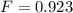
Calculate the rejection region;
But first, calculate the degrees of freedom
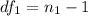
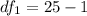
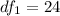
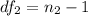
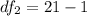
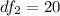
Using the F Distribution: table
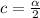
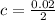
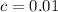
At 0.01 level (check row 20 and column 24), the critical value is:
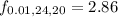 --- the upper bound
--- the upper bound
At 0.01 level (check row 24 and column 20), the critical value is:
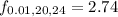
Calculate the inverse F distribution.
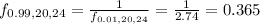 ---- the lower bound
---- the lower bound
The rejection region is then represented as:
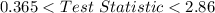
If the test statistic falls within this region, then the null hypothesis is rejected
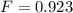 --- Test Statistic
--- Test Statistic
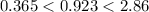
The above inequality is true; so, the null hypothesis is rejected.
This implies that, there is no sufficient evidence.