Answer:
a) C. 7.5 V
b) A. 2.5 V
Step-by-step explanation:
First, we find the total resistance of the circuit. A voltage divider circuit is a series circuit. Therefore, its total resistance will be the sum of individual resistances:
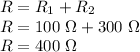
a)
Now, we will apply the voltage divider rule on this circuit to find the voltage across the 300 Ω Resistor (R₂):
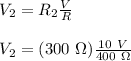
V₂ = 7.5 V
Therefore, the correct option is:
C. 7.5 V
b)
Now, the voltage across the 100 Ω Resistor (R₁) will be:
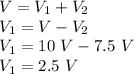
Therefore,the correct option is:
A. 2.5 V