Answer:
pH = 2.46
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, since this neutralization reaction may be assumed to occur in a 1:1 mole ratio between the base and the strong acid, it is possible to write the following moles and volume-concentrations relationship for the equivalence point:
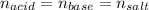
Whereas the moles of the salt are computed as shown below:
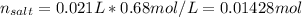
So we can divide those moles by the total volume (0.021L+0.0066L=0.0276L) to obtain the concentration of the final salt:
![[salt]=0.01428mol/0.0276L=0.517M](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/3av9lr9d0gg59pxkrj8mmy3x40n4phbfn3.png)
Now, we need to keep in mind that this is an acidic salt since the base is weak and the acid strong, so the determinant ionization is:
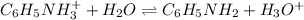
Whose equilibrium expression is:
![Ka=([C_6H_5NH_2][H_3O^+])/(C_6H_5NH_3^+)](https://img.qammunity.org/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/h4torak5asngzpktjbevslenodlhmb68da.png)
Now, since the Kb of C6H5NH2 is 4.3 x 10^-10, its Ka is 2.326x10^-5 (Kw/Kb), we can also write:
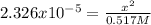
Whereas x is:
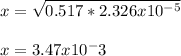
Which also equals the concentration of hydrogen ions; therefore, the pH at the equivalence point is:
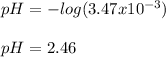
Regards!