Answer:
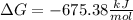
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
In this case, for this problem, it is possible to use the thermodynamic definition of the Gibbs free energy:
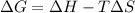
Whereas G, H and S can be assumed as constant over T; thus, we can calculate H at 135.4 °C:
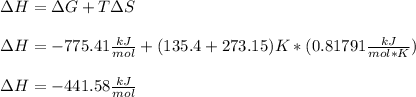
Now, we can calculate the Gibbs free energy at 12.7 °C as shown below:
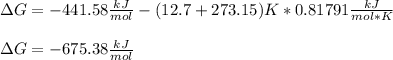
Best regards!