Answer:
![\displaystyle 3x - 2y = 13\:or\:y = 1(1)/(2)x - 6(1)/(2) \\ [0, -6(1)/(2)] \\ 1(1)/(2) = m]()
Explanation:
First, figure the rate of change [slope] out:
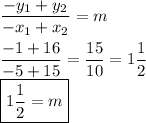
Now locate the initial value [y-intercept] by plugging an ordered pair into the slope-intercept formula. It does not matter which ordered pair you use:
_______________________________________________
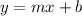
16 = 1½[15] + b >>
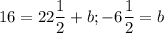
OR
1 = 1½[5] + b >>
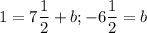
![\displaystyle [0, -6(1)/(2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/5cbiibgi3akjjy14ds2j696qlwjwjcmhtp.png)
_______________________________________________
You now have your initial value. All that is left is to write the equation of this line, which can be written two ways:
> Slope-Intercept Form
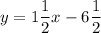
> Standard Form
![\displaystyle [Ax + By = C]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/vpy56xly6hb01i5r7gmgondtjp2xmysp7g.png)
y = 1½x - 6½
- 1½x - 1½x
___________
–1½x + y = –6½ [We CANNOT leave the equation this way, so multiply by –2 to eradicate the fraction\denominatour (if you wrote the equation as mixed numbers\if you wrote the equation as improper fractions).]
–2[–1½x + y = –6½]
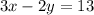
With that, you have defined all the information.
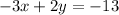
*About this equation, INSTEAD of multiplying by –2, you multiply by its oppocite, 2. Now, you can leave it like this, but UNIVERSALLY, the A-term is positive, so you must multiply the negative out as well.
I am joyous to assist you at any time.