Answer:
see explanation
Explanation:
1
the 2 legs of the triangle are congruent then the triangle is isosceles.
the segment from the vertex to the base is a perpendicular bisector, then
x = 6
using Pythagoras' identity in the lower right triangle to calculate the leg, which is the hypotenuse h
h² = 6² + 8² = 36 + 64 = 100 ( take square root of both sides )
h =
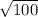 = 10
= 10
then
perimeter = 10 + 10 + 6 + 6 = 32
---------------------------------------------------------
2
Δ DFE and Δ HFG are similar by the AA postulate , then corresponding angles are congruent, so
∠ E = ∠ G , that is
6x - 4 = 5x + 4 ( subtract 5x from both sides )
x - 4 = 4 ( add 4 to both sides )
x = 8
then
∠ E = 6x - 4 = 6(8) - 4 = 48 - 4 = 44°
------------------------------------------------------------------
3
line P bisects XZ , then WX = 5
Δ XYZ is isosceles with XY = ZY
since perimeter = 36 then
XY = (36 - XZ) ÷ 2 = (36 - 10) ÷ 2 = 26 ÷ 2 = 13
using Pythagoras' identity in right triangle WXY
WY² + WX² = XY²
WY² + 5² = 13²
WY² + 25 = 169 ( subtract 25 from both sides )
WY² = 144 ( take square root of both sides )
WY =
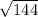 = 12
= 12
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
4
∠ ACB and ∠ BCD are a linear pair and sum to 180°
∠ ACB + 120° = 180° ( subtract 120° from both sides )
∠ ACB = 60°
since AC = BC then Δ ABC is isosceles with base angles congruent
∠ B = ∠ A
the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the 2 opposite interior angles.
∠ BCD is an exterior angle of the triangle , so
∠ A + ∠ B = 120° ( since ∠ A = ∠ B ) , then
2 ∠ B = 120° ( divide both sides by 2 )
∠ B = 60°
-----------------------------------------------------------------------
5
the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the 2 opposite interior angles.
∠ XYZ is an exterior angle of the triangle , then
15x - 18 = 5x + 2 + 8x + 4
15x - 18 = 13x + 6 ( subtract 13x from both sides )
2x - 18 = 6 ( add 18 to both sides )
2x = 24 ( divide both sides by 2 )
x = 12