Answer:
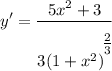
General Formulas and Concepts:
Pre-Algebra
Algebra I
- Functions
- Function Notation
- Exponential Rule [Root Rewrite]:
![\displaystyle \sqrt[n]{x} = x^{(1)/(n)}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/pi5gzwebrzl682dhc5849e.png)
Algebra II
- Logarithms and Natural Logs
- Logarithmic Property [Multiplying]:
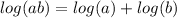
- Logarithmic Property [Exponential]:
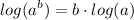
Calculus
Derivatives
Derivative Notation
Derivative Property [Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [cf(x)] = c \cdot f'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/sajvvpx1sytxjokl40ke2f.png)
Derivative Property [Addition/Subtraction]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(x) + g(x)] = (d)/(dx)[f(x)] + (d)/(dx)[g(x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/iqt7axoe8j2sh12ig7n0ah.png)
Basic Power Rule:
- f(x) = cxⁿ
- f’(x) = c·nxⁿ⁻¹
Derivative Rule [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[f(g(x))] =f'(g(x)) \cdot g'(x)](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/high-school/4e7e93dqa2auubmnlpfb3w.png)
Logarithmic Derivative:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx) [lnu] = (u')/(u)](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/owsup3ulao1pkiikfoff8q.png)
Implicit Differentiation
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
![\displaystyle y = x\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/53mytb1aya5mdsbv1i0bhg.png)
Step 2: Rewrite
- [Equality Property] ln both sides:
![\displaystyle lny = ln(x\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2})](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/1xc75z9uanxwguis4iq4ui.png)
- Logarithmic Property [Multiplying]:
![\displaystyle lny = ln(x) + ln(\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2})](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/l9fdbf5oveu816ijd6hzl6.png)
- Exponential Rule [Root Rewrite]:
![\displaystyle lny = ln(x) + ln \bigg[ (1 + x^2)^\bigg{(1)/(3)} \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/d0msw1mrb4g2bd4m3dtic1.png)
- Logarithmic Property [Exponential]:
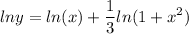
Step 3: Differentiate
- ln Derivative [Implicit Differentiation]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[lny] = (d)/(dx) \bigg[ ln(x) + (1)/(3)ln(1 + x^2) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/m7827lkv8g5j3wi3tzfzmz.png)
- Rewrite [Derivative Property - Addition]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[lny] = (d)/(dx)[ln(x)] + (d)/(dx) \bigg[ (1)/(3)ln(1 + x^2) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/r9q68ov7587sz6fxmupwu2.png)
- Rewrite [Derivative Property - Multiplied Constant]:
![\displaystyle (d)/(dx)[lny] = (d)/(dx)[ln(x)] + (1)/(3)(d)/(dx)[ln(1 + x^2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/j4a756r5e2cyu1qm8jxcyu.png)
- ln Derivative [Chain Rule]:
![\displaystyle (y')/(y) = (1)/(x) + (1)/(3) \bigg( (1)/(1 + x^2) \bigg) \cdot (d)/(dx)[(1 + x^2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/84nhr5txjb2hm47wbp16br.png)
- Rewrite [Derivative Property - Addition]:
![\displaystyle (y')/(y) = (1)/(x) + (1)/(3) \bigg( (1)/(1 + x^2) \bigg) \cdot \bigg( (d)/(dx)[1] + (d)/(dx)[x^2] \bigg)](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/uixtp0dh2tbijszt30e5pn.png)
- Basic Power Rule]:
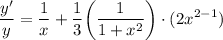
- Simplify:
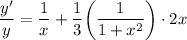
- Multiply:
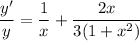
- [Multiplication Property of Equality] Isolate y':
![\displaystyle y' = y \bigg[ (1)/(x) + (2x)/(3(1 + x^2)) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/q8k6m4bo496qzhflch154a.png)
- Substitute in y:
![\displaystyle y' = x\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2} \bigg[ (1)/(x) + (2x)/(3(1 + x^2)) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/kd8ux9wxu0fcufsztjokm5.png)
- [Brackets] Add:
![\displaystyle y' = x\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2} \bigg[ (5x^2 + 3)/(3x(1 + x^2)) \bigg]](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/va8mkzeswyuip6h7f4ndwm.png)
- Multiply:
![\displaystyle y' = \frac{(5x^2 + 3)\sqrt[3]{1 + x^2}}{3(1 + x^2)}](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/mathematics/college/u1tihibn4rt3bsqw7yftd6.png)
- Simplify [Exponential Rule - Root Rewrite]:
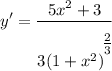
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Implicit Differentiation
Book: College Calculus 10e