Answer:
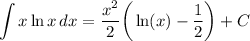
General Formulas and Concepts:
Calculus
Differentiation
- Derivatives
- Derivative Notation
Integration
- Integrals
- [Indefinite Integrals] Integration Constant C
Integration Rule [Reverse Power Rule]:
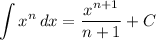
Integration by Parts:
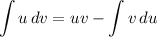
- [IBP] LIPET: Logs, inverses, Polynomials, Exponentials, Trig
Explanation:
Step 1: Define
Identify
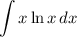
Step 2: Integrate Pt. 1
Identify variables for integration by parts using LIPET.
- Set u:
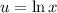
- [u] Logarithmic Differentiation:
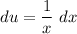
- Set dv:
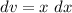
- [dv] Integration Rule [Reverse Power Rule]:
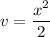
Step 3: Integrate Pt. 2
- [Integral] Integration by Parts:
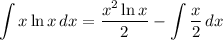
- [Integral] Rewrite [Integration Property - Multiplied Constant]:
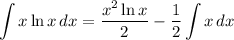
- Factor:
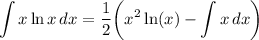
- [Integral] Integration Rule [Reverse Power Rule]:
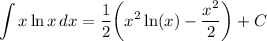
- Factor:
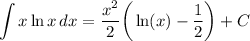
Topic: AP Calculus AB/BC (Calculus I/I + II)
Unit: Integration