Answer:
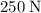 (downwards.)
(downwards.)
Approximately
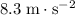
(Assuming that the gravitational field strength is
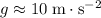 .)
.)
Step-by-step explanation:
Note that
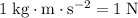 .
.
There are two forces on this object:
- weight (downward), and
- air resistance (upwards.)
Let
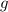 denote the gravitational field strength. The weight of an object of mass
denote the gravitational field strength. The weight of an object of mass
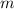 will be
will be
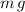 .
.
In this example, since
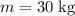 and
and
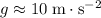 around the surface of the earth. The weight of this object will be:
around the surface of the earth. The weight of this object will be:
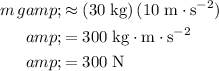 .
.
The air resistance on this object is given to be
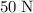 (upwards.) Since the two forces are in opposite directions, the magnitude of the resultant force on the object will be the difference between their magnitudes:
(upwards.) Since the two forces are in opposite directions, the magnitude of the resultant force on the object will be the difference between their magnitudes:
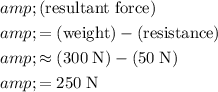 .
.
(Downwards.)
Divide the resultant force on the object by the mass
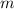 of the object to find the acceleration of the object:
of the object to find the acceleration of the object:
 .
.