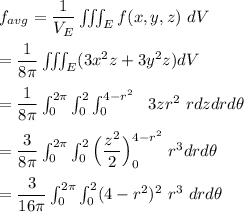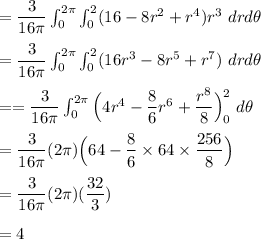Answer:
The average function
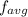 value = 4
value = 4
Explanation:
Given that:
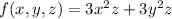
The enclosed region
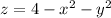 and the plane z = 0.
and the plane z = 0.
Over an area E, the average value of a function f(x,y,z) is:
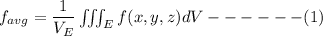
where;
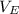 = volume of region E
= volume of region E
To find the volume use cylindrical coordinates;
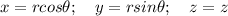
Then;
E = 0 ≤ r ≤2, 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π, 0 ≤ z ≤ 4 - r²
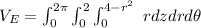
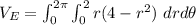
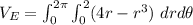
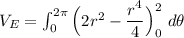
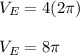
However, from equation (1):