Answer: The temperature that is needed to reach this pressure is
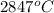 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the temperature with changing pressure, we use the equation given by Gay Lussac law.
This law states that pressure is directly proportional to the temperature of the gas at constant volume and the number of moles.
Mathematically,
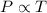 (At constant volume and number of moles)
(At constant volume and number of moles)
The equation given by this law is:
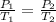
where,
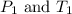 are initial pressure and temperature
are initial pressure and temperature
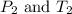 are final pressure and temperature
are final pressure and temperature
Given values:
![P_1=775 torr\\T_1=39^oC=[39+273]K=312K\\P_2=7750 torr\\T_2=?](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/zpvvlcrljnve73gzm39r21.png)
Plugging values in the above equation:
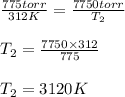
Converting it into degree Celsius:

Hence, the temperature that is needed to reach this pressure is
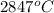 .
.