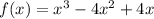As we can see on the picture, the graphs crosses the x-axis at x=0 and it bounces of the x-axis at x=2. In the first case, the polynomial has a factor of degree 1 at x=0. In the second case, the factor has a degree 2 at x=2. So, we can write the following:
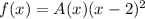
where A is a constant to be determined. We can find this constant by noticing that when x=3, f(3)=3, then we have
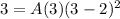
which gives
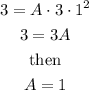
Therefore, we get
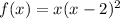
Now, lets expand this result. By
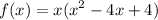
then, the answer is