Step-by-step explanation:
From the question, we have a point and the slope of the line given.
To get the equation of line, a point slope equation will be used:
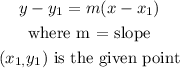
Given point: (-7, 4)
m = 0
substitute in the equation:
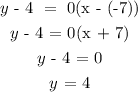
Note: whenever the slope of a line is zero, the equation will be in the form y = b
where b is the value of the y coordinate of the given point. Also th