The height of the ball, h in meters, is modeled by the next equation:
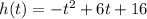
where t is time in seconds.
a. At t = 0, the height of the ball is equal to the height of the cliff. Substituting t = 0 into the equation, we get:
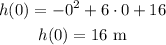
The height of the cliff is 16 m.
b. When the ball hits the ground, h(t) = 0. Then, we need to find the zeros of the polynomial. Using the quadratic formula with a = -1, b = 6, and c = 16, we get:
![\begin{gathered} t_(1,2)=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a} \\ t_(1,2)=\frac{-6\pm\sqrt[]{6^2-4\cdot(-1)\cdot16}}{2\cdot(-1)} \\ t_(1,2)=\frac{-6\pm\sqrt[]{100}}{-2} \\ t_1=(-6+10)/(-2)=-2 \\ t_2=(-6-10)/(-2)=8 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/5jh0ce2jsvvvkwqo8z1v5lqnpekbcdwl0b.png)
In the context of the problem, a negative value has no sense, then t = -2 is discarded.
The ball hits the ground after 8 seconds.
c. The maximum height of the ball corresponds to the vertex of the parabola. The x-coordinate of the vertex, which in this case corresponds to variable time, is computed as follows:
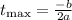
Substituting with a = -1, and b = 6, we get:
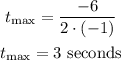
The height of the ball at t = 3 is:
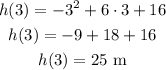
The maximum height of the ball is 25 m. This height is reached after 3 seconds.