Answer:
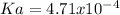
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello there!
In this case, according to the Henderson-Hasselbach equation, it is possible to write:
![pH=pKa+log(([A^-])/([HA]) )](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/nopdsa2onnn7y80awkujbe.png)
Next, since we are given the pH and the [A–]/[HA] ratio, we can solve for the pKa as shown below:
![pKa=pH-log(([A^-])/([HA]) )](https://img.qammunity.org/qa-images/2022/formulas/chemistry/college/lkz07pkqd6yv8k3bzks0fi.png)
Now, we plug in the values to obtain:
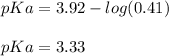
Next, Ka is:
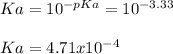
Best regards!