The given problem can be exemplified in the following diagram:
In the diagram we have the following forces:

Now we will determine the value of the acceleration of the box. To do that we will add the forces in the horizontal direction:
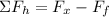
According to Newton's second law we have that the sum of forces must be equal to the product of the mass and the acceleration:
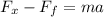
To determine the value of the friction force we use the following relationship:
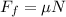
To determine the value of the normal force we add the forces in the vertical direction:
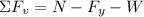
Since there is no movement in the vertical direction we have:
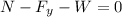
Now we solve for the normal force:
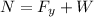
To determine the vertical component of the force we use the right triangle shown in the diagram. We use the function sine and we get:
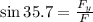
Now we multiply both sides by "F":
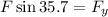
Now we substitute this value in the formula for the normal force:
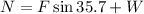
Now we substitute this value in the formula for the friction force:
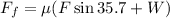
Now we substitute this value in the formula for the horizontal forces:
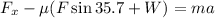
Now, to determine the horizontal component of the force we use the function cosine:
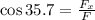
Now we multiply both sides by "F":
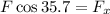
Now we substitute in the sum of horizontal forces:
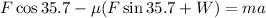
Now we solve for "a" by dividing both sides by "m":
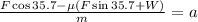
To determine the mass we use the formula for the weight:
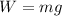
Where:
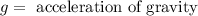
Now we divide both sides by "g";
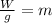
Now we substitute the values:
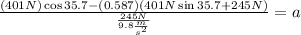
Solving the operations we get:
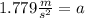
Now, we will determine the final velocity of the movement. We will use the following equation of motion:
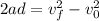
Since the box starts from rest this means that the initial velocity is zero:
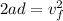
Now we take the square root to both sides:
![\sqrt[]{2ad}=v_f](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/p0svh5lta7gkpjei5wk7f50femsehroo98.png)
Now we substitute the values:
![\sqrt[]{2(1.779(m)/(s^2))(3.37m)}=v_f](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/n5pi9relnha52iqry5wj1if84boct327hd.png)
Solving the operations:
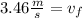
Now we use the following equation of motion to determine the time:
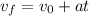
Since the initial velocity is zero:
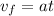
Now we divide by the acceleration:
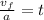
Substituting the values:
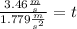
Solving the operations:
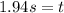
Therefore, it takes the box 1.94 seconds to move.