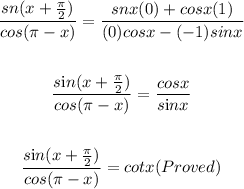To prove:
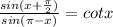
Note that:
sin(A + B) = sinAcosB + cosAsinB
sin(A - B) = sinAcosB - cosAsinB
Applying these rules to the given trigonometric expression
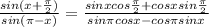
Note that:
cos(π) = -1
cos(π/2) = 0
sin(π) = 0
sin(π/2) = 1
Substitute these values into the expression above