Part a.
In this case, we need to substitute the given point values into the expression x-2y. Then for point (7,3), we have
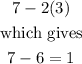
Now, for point (7,5) we have
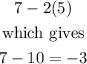
Part b.
As we can note, in the first case we got 1 which is 2 units from 3. In the second case, we got -3, which is 6 units from 3. Therefore, point (7,3) gives the closest value to 3