Answer:
(-3/5, 4/5)
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the system of equations:
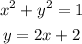
First, we substitute y=2x+2 into the first equation to obtain:
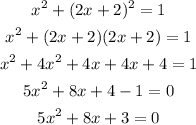
We solve the derived quadratic equation for x,
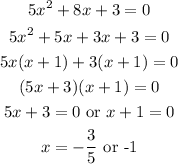
We then solve for the corresponding values of y using any of the equations.
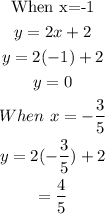
Therefore, the solutions o this system are:
(-1,0) and (-3/5, 4/5).
The other solution is (-3/5, 4/5).