18) Notice that angles (11y-32)° and (6x+7)° are opposite with respect to the vertex, then they are congruent.
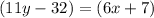
On the other hand, consider any of the angles that are formed by the same vertex as (11y-32)° and (6x+7)°. Any of those is congruent with the angle (3x-16)° (One by the corresponding relation and the other by being alternate exterior angles).
Therefore:
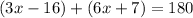
With those two equations, we can solve for x and y as follows:
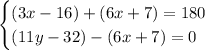
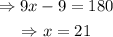
Therefore, x=21°
As for y:
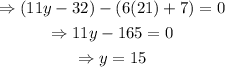
Then, y=15°
19) Notice that angles (8x-14)° and (5y+16)° are supplementary, then:
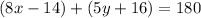
And angles (8x-14)° and (5x+34)° are alternate exterior angles, thus they are congruent:
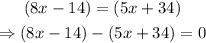
The system of equations is:

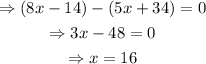
x=16°
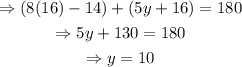
y=10°
20) Notice that angles (5y-23)° and (3x)° are generated by the same transversal line and that they are corresponding angles. Therefore,
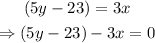
Notice that angles (2x+13)° and (3x+47)° are supplementary, as the figure below shows:
The angles in the same color are congruent.
Then, we get the following system of equations:
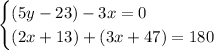
Solving for x and y:
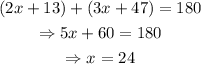
The answer is x=24°
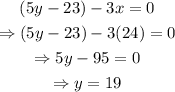
The answer is y=19°